Ovarian Cancer: Understanding the Silent Killer
Ovarian Cancer is one of the most serious health threats to women worldwide. Known as the "silent killer," it often goes undetected until it reaches advanced stages. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and effective management.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
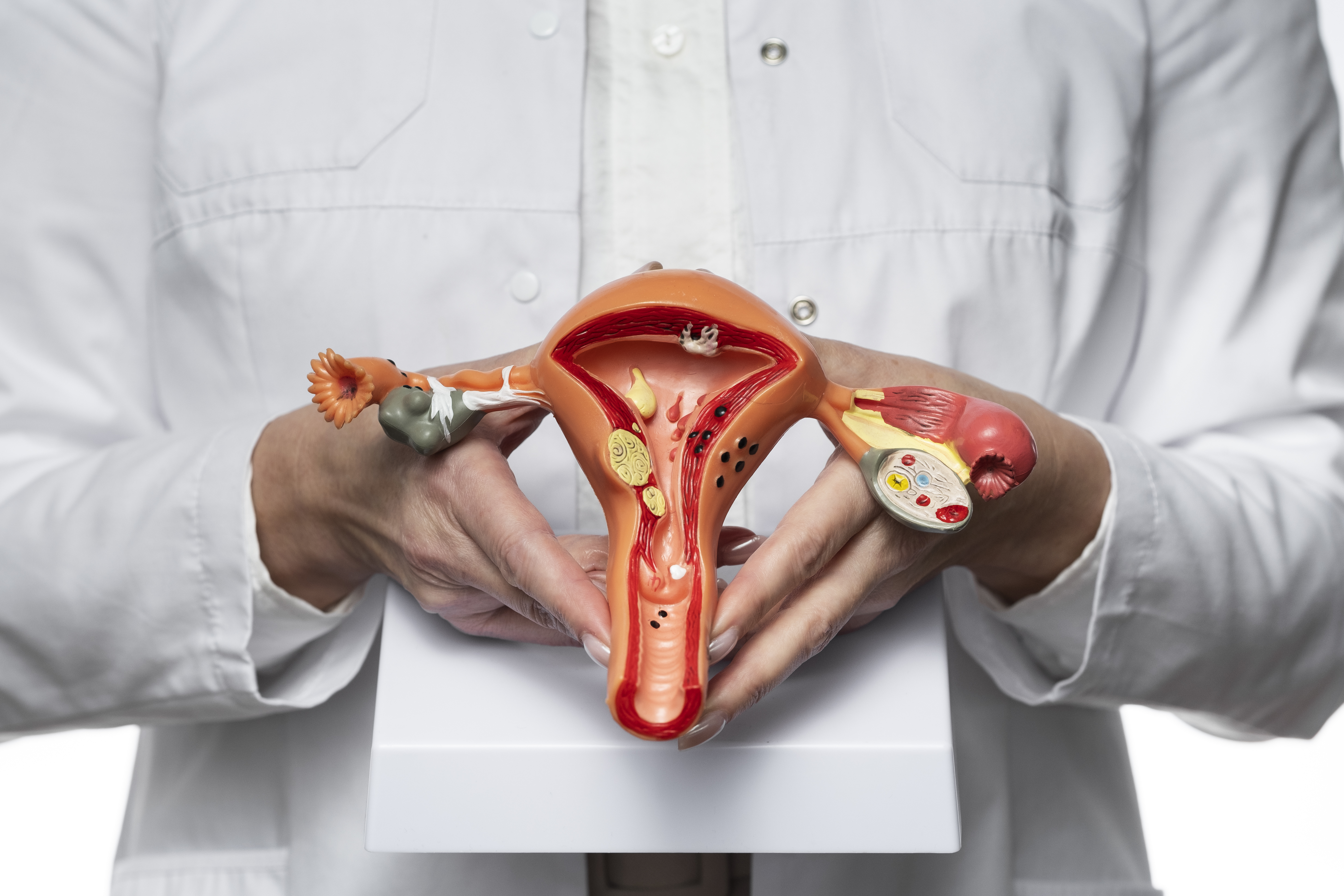
Ovarian cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the ovary begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. If not treated in time, these cancerous cells can spread to other parts of the body. The ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system, produce eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Types of Ovarian Cancer:
Ovarian cancer is classified into three main types based on the cells where the cancer originates:
-
1. Epithelial Ovarian Cancer:
The most common type, accounting for about 90% of cases. It starts in the layer of cells covering the ovaries.
-
2. Germ Cell Ovarian Cancer:
A rare type that originates from egg-producing cells.
-
3.Stromal Ovarian Cancer:
Arises from the connective tissue that holds the ovary together and produces hormones.
Causes and Risk Factors of colorectal cancer:
The exact cause of ovarian cancer remains unknown, but several factors increase the risk, including:
- 1. Age:Women over 50, particularly post-menopausal women, are more susceptible.
- 2. Family History: A history of ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer in the family raises the risk.
- 3. Physical Inactivity:BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations are linked to a higher risk.
- 4. Alcohol Consumption:Women with endometriosis have an increased likelihood of developing ovarian cancer.
- 5. Obesity: Women who have never been pregnant or had their first child after 35 may be at higher risk.
Symptoms to Watch For:
Ovarian cancer is difficult to diagnose early because its symptoms mimic common gastrointestinal and bladder problems. However, persistent symptoms such as:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Feeling full quickly while eating
- Frequent urination
- Changes in bowel habits
- Unexplained weight loss or gain should not be ignored, especially if they last for more than two weeks.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage of cancer and overall health condition of the patient. The main treatments include:
- 1. Surgery:To remove the tumor or, in advanced cases, both ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the uterus.
- 2. Chemotherapy:Uses drugs to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors before surgery.
- 3. Targeted Therapy:Attacks specific weaknesses in cancer cells.
- 4. Radiation Therapy: Less commonly used but can help control symptoms.
- 5. Hormone Therapy: Used in rare cases where cancer is hormone-sensitive.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer is a serious but manageable disease if detected early. Raising awareness, understanding risk factors, and recognizing symptoms can help women take proactive steps towards their health. If you experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Early detection can save lives.